Diagnostic Ultrasound
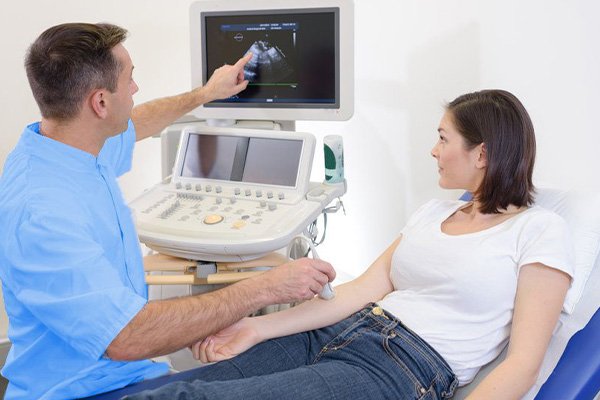
Applications in Central Diagnostics
Abdominal Imaging: Diagnostic ultrasound is commonly used to examine organs in the abdominal region, including the liver, gallbladder, pancreas, spleen, kidneys, and intestines. It aids in the detection of abnormalities like tumors, cysts, and organ enlargement, helping physicians make accurate diagnoses.
Cardiac Evaluation: Echocardiography, a specialized form of ultrasound, plays a pivotal role in assessing the heart’s structure and function. It enables the visualization of the heart’s chambers, valves, and blood flow, aiding in the diagnosis of various cardiovascular conditions, such as heart disease and heart valve abnormalities.
Neuroimaging: In central nervous system diagnostics, ultrasound can provide valuable information about brain and spinal cord abnormalities. It aids in detecting tumors, bleeding, hydrocephalus, and congenital malformations, assisting neurologists and neurosurgeons in making critical decisions.
Vascular Studies: Doppler ultrasound, a specialized technique, is used to assess blood flow through blood vessels. It helps diagnose conditions like deep vein thrombosis (DVT), peripheral artery disease (PAD), and carotid artery stenosis, allowing for prompt intervention and management.
Benefits of Diagnostic Ultrasound
Non-Invasive: One of the primary advantages of diagnostic ultrasound is that it is non-invasive, meaning it does not require surgical incisions or radiation exposure. This makes it a safe and painless imaging modality for patients of all ages, including infants and pregnant women.
Real-Time Imaging: Unlike other imaging techniques such as X-rays or MRI, ultrasound provides real-time imaging, allowing clinicians to observe the movement of organs and blood flow as it happens. This dynamic visualization can be crucial in diagnosing certain conditions.
Cost-Effective: Diagnostic ultrasound is generally more cost-effective than other imaging modalities, making it accessible to a broader range of patients and healthcare facilities.
Portable and Versatile: Modern ultrasound machines are portable and versatile, enabling point-of-care imaging in various clinical settings, including emergency rooms, ambulances, and rural healthcare facilities.
