Fetal echocardiography
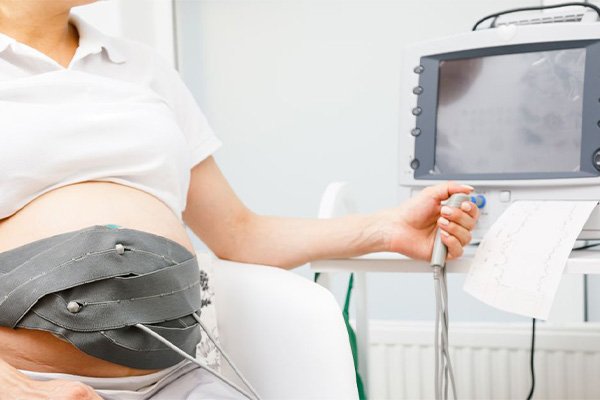
How Fetal Echocardiography Works
Fetal echocardiography is performed using ultrasound technology similar to routine prenatal sonography. However, it requires specialized training and expertise to visualize the intricate structures of the fetal heart accurately. During the procedure, a transducer is placed on the mother’s abdomen to emit high-frequency sound waves into the womb. These sound waves bounce off the fetal heart and surrounding structures, creating detailed images that are then analyzed by a skilled sonographer or a fetal cardiologist.
Applications of Fetal Echocardiography
Detecting Congenital Heart Defects: Fetal echocardiography is primarily used to identify and assess congenital heart defects and abnormalities in the fetal heart’s structure. It can help detect conditions such as ventricular septal defects, atrial septal defects, tetralogy of Fallot, transposition of the great arteries, and many others.
Assessing Cardiac Function: Fetal echocardiography also evaluates the heart’s function, including the assessment of blood flow, heart rate, and heart rhythm, providing crucial information about the baby’s overall cardiac health.
Monitoring Heart Development: The imaging capabilities of fetal echocardiography allow healthcare providers to monitor the fetal heart’s development over time, ensuring that any potential issues are detected early and managed appropriately.
Applications of Fetal Echocardiography
Detecting Congenital Heart Defects: Fetal echocardiography is primarily used to identify and assess congenital heart defects and abnormalities in the fetal heart’s structure. It can help detect conditions such as ventricular septal defects, atrial septal defects, tetralogy of Fallot, transposition of the great arteries, and many others.
Assessing Cardiac Function: Fetal echocardiography also evaluates the heart’s function, including the assessment of blood flow, heart rate, and heart rhythm, providing crucial information about the baby’s overall cardiac health.
Monitoring Heart Development: The imaging capabilities of fetal echocardiography allow healthcare providers to monitor the fetal heart’s development over time, ensuring that any potential issues are detected early and managed appropriately.
